Question
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters. For example, the longest substring without repeating letters for "abcabcbb" is "abc", which the length is 3. For "bbbbb" the longest substring is "b", with the length of 1.
Stats
| Frequency | 2 |
| Diffficulty | 3 |
| Adjusted Difficulty | 4 |
| Time to use | ---------- |
Ratings/Color = 1(white) 2(lime) 3(yellow) 4/5(red)
Analysis
This question looks easy (well, isn’t it?), but it really is not easy!.
The main idea is: an array of int(128) is used to keep track of the last occurance position of each character. So we iterate thru the characters while constently checking the last occurrence of the letter. Meanwhile, keep updating the longest distance.
There is 1 place where it’s extremely easy to make mistake, that is the condition of update left points:
if (previousPos != -1&& previousPos >= left) {
left = previousPos + 1;
}
If you have an idea of using array int(128) to store last occurrence, and you got the above if condition correct, then you nailed it!
Again, this is a tough question. There’s a seemingly more intuitive solution using the sliding window method. It’s very similar to [LeetCode 76] Minimum Window Substring.
Solution
Note what happens when a repeating char is found (2 different conditions).
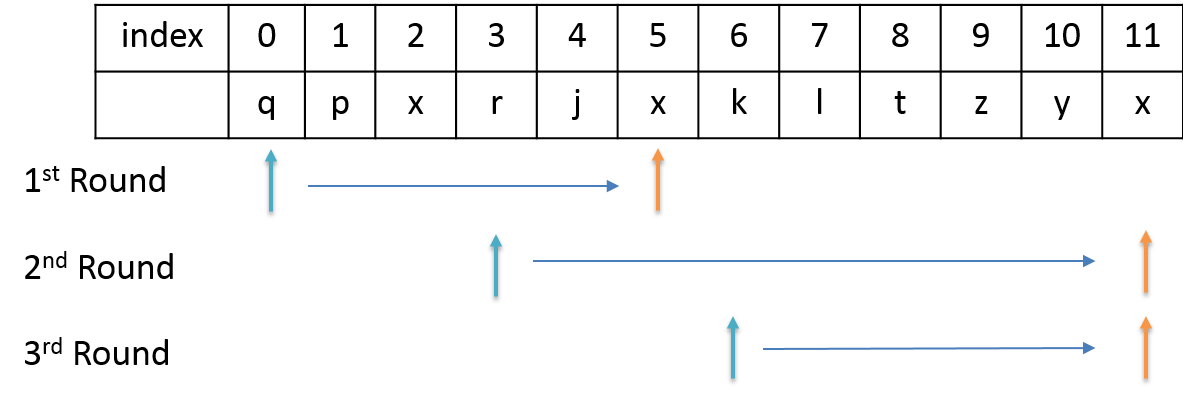
My code
The proper way:
public class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] flag = new int[128];
for (int i = 0; i < flag.length; i++) {
flag[i] = -1;
}
// left and right pointer defines the valid range
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
int longest = 0;
int len = s.length();
while (right < len) {
char letter = s.charAt(right);
int previousPos = flag[letter];
if (previousPos != -1&& previousPos >= left) {
// if right pointer points to an old letter, and is within current range
// then we need to update our left pointer:
// to bypass the previous occurrence of that letter
left = previousPos + 1;
}
flag[letter] = right;
// advance right pointer to the next letter, and calculate longest distance
right++;
longest = Math.max(longest, right - left);
}
return longest;
}
}
The sliding window way:
public class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int len = s.length();
int left = 0;
int right = 1;
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<Character>();
set.add(s.charAt(0));
int longest = 1;
while (right < len) {
// right pointer proceeds until boundary or duplicate char found
while (right < len && !set.contains(s.charAt(right))) {
set.add(s.charAt(right));
right++;
longest = Math.max(longest, right - left);
}
if (right == len) {
return longest;
} else {
// right pointer has reached a duplicate char.
// now move left pointer until that dup char is found
while (s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) {
set.remove(s.charAt(left));
left++;
}
// left pointer advance by one to bypass the dup char
left++;
// right pointer advance by one to include the dup char
right++;
}
}
return Math.max(longest, right - left);
}
}