First Word
LinkedList aims to test one of the most important concepts in C++, pointers.
Unlike array, linked list does not have ‘in-place’ operations. This is very important to understand.
Type 1: Dummy Node
When the head is not determined, use DummyHead.
Note that when using DummyHead to solve problems, the pointer starts from DummyHead. By doing this, we assuming that DummyHead must be valid, and we only check pointer.next (instead of checking pointer itself). See ‘Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II’ for details.
Type 2: Five Basic Operations in Linked List
- Insert in Sorted List
- Remove in Sorted List
- Reverse a list
- Merge 2 Sorted List
- Find middle
1.Insert in Sorted List
public ListNode insert(ListNode head, ListNode node) {
// first, initialize
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
dummy.next = head;
// second, assume p is less than node, and check p.next
ListNode p = dummy;
while (p.next != null && p.next.val < node.val) {
p = p.next;
}
// insert node after 'p'
node.next = p.next;
p.next = node;
return dummy.next;
}
2.Remove in Sorted List
(written by me)
public ListNode remove(ListNode head, int value) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode p = dummy;
while (p.next != null && p.next.val != value) {
p = p.next;
}
if (p.next != null && p.next.val == value) {
while (p.next != null && p.next.val == value)
p.next = p.next.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
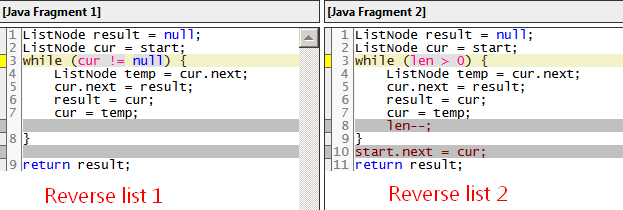
3.Reverse a list
First variant: Reverse from a particular node to the end.
四句话 statement.
public ListNode reverse(ListNode start) {
ListNode result = null;
ListNode cur = start;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = result;
result = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return result;
}
Second variant: Reverse from a node until another node
// Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, start = 2 and len = 3,
// return 1->4->3->2->5->NULL.
public ListNode reverseRange(ListNode start, int len) {
ListNode result = null;
ListNode cur = start;
while (len > 0) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = result;
result = cur;
cur = temp;
len--;
}
start.next = cur;
return result;
}
The comparison:
More: there is a way to reverse list recursively. This can be another good interview question. Reverse linkedlist recursively
4.Merge 2 Sorted List
public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {
if (head1.val < head2.val) {
p.next = head1;
head1 = head1.next;
p = p.next;
} else {
p.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
p = p.next;
}
}
if (head1 == null) {
p.next = head2;
} else {
p.next = head1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
5.Find middle
There are 2 ways to do this: calculate the total length, or fast/slow pointer. But fast/slow pointer is better because in engineering world, a lot of problems only allows information to flow once (数据流概念). Sometimes it’s not a good idea to read list for a second (or 1.5) time.
public ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
Dummy head questions
5 basic operations questions
Reverse Linked List II - difficult
-
2 operations used
-
3 operations used
-
For this question, it’s important to write a comparator by yourself, to show your understanding of a PriorityQueue.
nklgk time, why? 1:14:30 recording about heap 1:15:00 recording
Code
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
Easy, no dummy head needed.
Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode p = dummy;
while (p.next != null && p.next.next != null) {
if (p.next.val == p.next.next.val) {
int dupVal = p.next.val;
while (p.next != null && p.next.val == dupVal) {
p.next = p.next.next;
}
} else {
p = p.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
Partition List - spend a lot of time on a list cycle in the result
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode head1 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p1 = head1;
ListNode p2 = head2;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < x) {
p1.next = cur;
p1 = cur;
} else {
p2.next = cur;
p2 = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
p1.next = head2.next;
// VERY IMPORTANT THIS LINE !!!
p2.next = null;
// VERY IMPORTANT THIS LINE !!!
return head1.next;
}
Merge Two Sorted Lists
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
p.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
p = p.next;
} else {
p.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
p = p.next;
}
}
if (l1 == null) {
p.next = l2;
} else {
p.next = l1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
5 basic operations
Reverse Linked List II
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode start = dummy;
int count = 1;
while (head != null && count < m) {
start = start.next;
count++;
}
start.next = reverseRange(start.next, n - m + 1);
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverseRange(ListNode start, int len) {
ListNode result = null;
ListNode cur = start;
while (len > 0) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = result;
result = cur;
cur = temp;
len--;
}
start.next = cur;
return result;
}
Sort List
Time complexity analysis: T(n) = 2 T(n/2) + O(n). By applying Master theorem, time = O(nlgn).
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode mid = findMid(head);
ListNode secondHalf = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
head = sortList(head);
secondHalf = sortList(secondHalf);
return merge(head, secondHalf);
}
private ListNode findMid(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode h1, ListNode h2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
while (h1 != null && h2 != null) {
if (h1.val < h2.val) {
p.next = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
} else {
p.next = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if (h1 == null) {
p.next = h2;
} else if (h2 == null) {
p.next = h1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
Reorder List
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return;
}
ListNode mid = findMid(head);
ListNode secondHalf = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
secondHalf = reverse(secondHalf);
head = mergeInterlace(head, secondHalf);
}
private ListNode findMid(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode result = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = result;
result = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return result;
}
private ListNode mergeInterlace(ListNode h1, ListNode h2) {
ListNode result = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
ListNode p = result;
while (h1 != null && h2 != null) {
p.next = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
p.next.next = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
p = p.next.next;
}
if (h1 == null) {
p.next = h2;
} else {
p.next = h1;
}
return result;
}
Linked List Cycle
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return false;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Linked List Cycle II
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
Merge k Sorted Lists
I write the code in the original post.
Copy List with Random Pointer
public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// 1, make a new copy of each node
RandomListNode p = head;
while (p != null) {
RandomListNode copy = new RandomListNode(p.label);
copy.next = p.next;
p.next = copy;
p = copy.next;
}
// 2. link the random pointer of copied nodes
p = head;
while (p != null) {
if (p.random != null) {
p.next.random = p.random.next;
}
p = p.next.next;
}
// 3. break the copied nodes from original nodes
RandomListNode result = head.next;
p = head;
RandomListNode p2 = head.next;
while (p != null) {
p.next = p2.next;
if (p2.next != null) {
p2.next = p2.next.next;
}
p = p.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
return result;
}