Overview
Cryptographic hash function is a hash function which is considered practically impossible to invert.
The input is arbitrary length, and output is fixed length.
The input is called ‘message’ and output (the hash value) is called ‘digest’.
Common examples are:
- MD5
- 128-bit (16-byte) hash value, typically expressed with 32 digit hex number
- have colllision attack risks
- SHA-1 (said to be better than MD5)
- 160-bit (20-byte) hash value, typically expressed with 40 digit hex number
- No known collision found so far
Properties
- Computationally efficient
- Collision resistant
- Hide information
- Look random
Examples
I generated checksum values on an important file I backed up to ensure that everything went OK. source
To verify that the latest version of Firefox I was downloading is correct, I ran a cryptographic hash function, SHA-1 to be exact, on the download and compared that checksum with the one published on Mozilla’s site. source
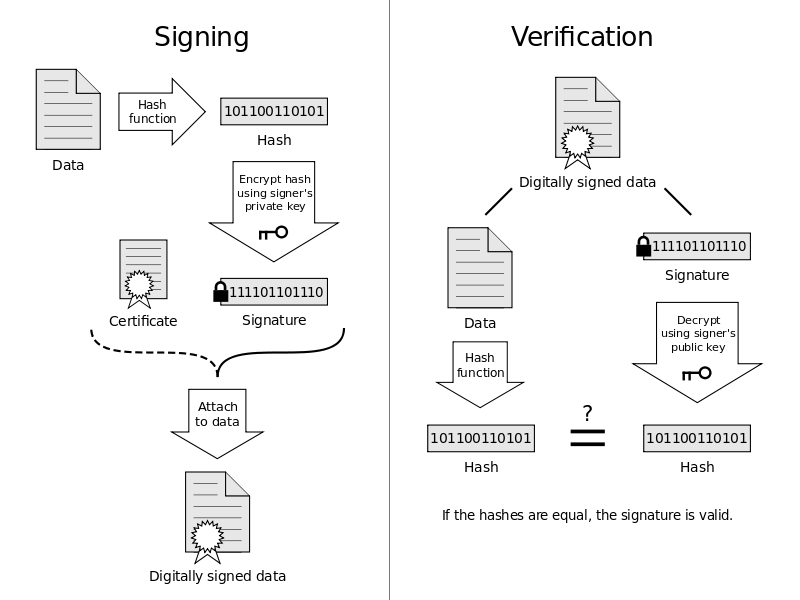
Digital signature
Digital signature is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message. It uses public/private keys.
In practice, the signature is not used directly on the file, but rather on the digest of the file.
Video on digital signature.