Blocking Queue Implementation
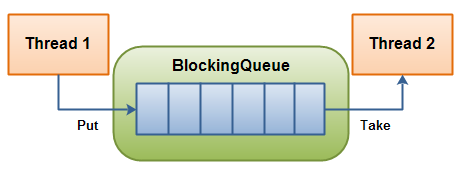
A blocking queue is a queue, so we init a queue with a pre-defined size.
BlockingQueue Class comes with Java 5, in java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue. This example is only used to help you understand what’s happening behind the scene.
Both enqueue(Object o){} and dequeue(){} are synchronized method.
Both methods do while { wait(); } and then notifyAll().
Code
public class MyBlockingQueue {
private List<Object> queue = new LinkedList<Object>();
private int size = 10;
public MyBlockingQueue(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public synchronized void enqueue(Object item) throws InterruptedException {
while (this.queue.size() == this.size) {
wait();
}
if (this.queue.size() == 0) {
notifyAll();
}
this.queue.add(item);
}
public synchronized Object dequeue() throws InterruptedException {
while (this.queue.size() == 0) {
wait();
}
if (this.queue.size() == this.size) {
notifyAll();
}
return this.queue.remove(0);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.queue.isEmpty();
}
}
Another example
This BlockingQueue example makes use MyBlockingQueue that we defined above.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue(1024);
Producer producer = new Producer(queue);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(queue);
new Thread(producer).start();
new Thread(consumer).start();
Thread.sleep(4000);
}
}
Producer
public class Producer implements Runnable {
protected MyBlockingQueue queue = null;
public Producer(MyBlockingQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("Producer starting... ");
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
queue.enqueue("" + i);
Thread.sleep(500);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Consumer
public class Consumer implements Runnable {
protected MyBlockingQueue queue = null;
public Consumer(MyBlockingQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Consumer finished. ");
}
}
Output:
Producer starting...
1
2
3
4
5
Consumer finished.