Graph
For graph, there are only 2 high-frequency questions, which is ‘clone graph’ and ‘topology sorting’.
Question list
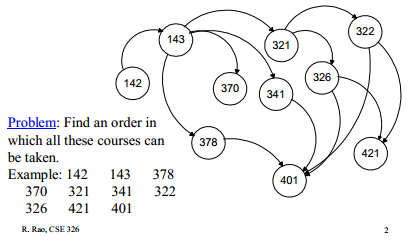
Clone Graph - difficult
Topology Sorting
Search
Search have either DFS or BFS.
First, we will cover permutations and combinations using DFS. In this section we solve the famous N-queens question.
Then, there’s a few BFS questions. Graph traversal is BFS, and Word ladder is also a classic BFS question.
Question list
Subsets
Subsets II
difficult
Permutations
Permutations II - difficult
N-Queens
how to use hashmap (and some space) to make it faster? 3 hashmaps to store the row, the (x,y) diff and sum. This will make isValid() method O(1).
N-Queens II
Next Permutation
Previous Permutation
Palindrome Partitioning
Palindrome Partitioning II
Combination Sum
Combination Sum II
Word Ladder
Word Ladder II
Additional questions
Restore IP Addresses
Combinations
Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
Permutation Sequence
Code
Graph
Clone Graph
public UndirectedGraphNode cloneGraph(UndirectedGraphNode node) {
if (node == null) return null;
HashMap<UndirectedGraphNode, UndirectedGraphNode> map =
new HashMap<UndirectedGraphNode, UndirectedGraphNode>();
Queue<UndirectedGraphNode> queue = new LinkedList<UndirectedGraphNode>();
map.put(node, new UndirectedGraphNode(node.label));
queue.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
UndirectedGraphNode cur = queue.remove();
UndirectedGraphNode copy = map.get(cur);
// here the 'copy' must exist. why? because all neighbors
// has been added to the map when they're pushed to queue.
// so 'cur' must have a corresponding copy in the hashmap.
for (UndirectedGraphNode neib: cur.neighbors) {
if (!map.containsKey(neib)) {
queue.add(neib);
map.put(neib, new UndirectedGraphNode(neib.label));
}
copy.neighbors.add(map.get(neib));
}
}
return map.get(node);
}
Topology Sorting
A new post is written for it.
Search
Subsets
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (num == null || num.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(num);
helper(ans, new LinkedList<Integer>(), num, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path, int[] num, int pos) {
ans.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
for (int i = pos; i < num.length; i++) {
path.add(num[i]);
helper(ans, path, num, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
Subsets II
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (num == null || num.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(num);
helper(ans, new LinkedList<Integer>(), num, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path, int[] num, int pos) {
ans.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
for (int i = pos; i < num.length; i++) {
if (i > pos && num[i - 1] == num[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(num[i]);
helper(ans, path, num, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
Permutations
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (num == null || num.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
helper(ans, new LinkedList<Integer>(), num);
return ans;
}
private void helper(List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path, int[] num){
if (path.size() == num.length) {
ans.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (path.contains(num[i])) {
continue;
}
path.add(num[i]);
helper(ans, path, num);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
Permutations II
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] num) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (num == null || num.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(num);
helper(ans, new LinkedList<Integer>(), num, new int[num.length]);
return ans;
}
private void helper(List<List<Integer>> ans, List<Integer> path, int[] num, int[] visited){
if (path.size() == num.length) {
ans.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == 1) {
continue;
}
if (i > 0 && visited[i - 1] == 1 && visited[i] == 0 && num[i - 1] == num[i]) {
// if current number is same as previous, then don't visit current
continue;
}
path.add(num[i]);
visited[i] = 1;
helper(ans, path, num, visited);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
visited[i] = 0;
}
}
N-Queens
一次通关!高兴。
public List<String[]> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<String[]> ans = new LinkedList<String[]>();
if (n <= 0) {
return ans;
}
helper(ans, new int[n], n, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(List<String[]> ans, int[] path, int n, int pos) {
if (pos >= n) {
ans.add(convert(path, n));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
path[pos] = i;
if (!isValid(path, pos)) {
continue;
}
helper(ans, path, n, pos + 1);
}
}
private String[] convert(int[] path, int n) {
String[] ans = new String[n];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
ans[j] = "";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans[j] += (j == path[i]) ? 'Q' : '.';
}
}
return ans;
}
private boolean isValid(int[] path, int pos) {
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
// check path[i] and path[pos]
if (path[i] == path[pos]) {
return false;
}
if (path[i] - path[pos] == pos - i) {
return false;
}
if (path[pos] - path[i] == pos - i) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
N-Queens II
int total;
public int totalNQueens(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
helper(new int[n], n, 0);
return total;
}
private void helper(int[] path, int n, int pos) {
if (pos >= n) {
total++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
path[pos] = i;
if (!isValid(path, pos)) {
continue;
}
helper(path, n, pos + 1);
}
}
private boolean isValid(int[] path, int pos) {
for (int i = 0; i < pos; i++) {
// check path[i] and path[pos]
if (path[i] == path[pos]) {
return false;
}
if (path[i] - path[pos] == pos - i) {
return false;
}
if (path[pos] - path[i] == pos - i) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
Next Permutation
public void nextPermutation(int[] num) {
if (num == null || num.length <= 1) {
return;
}
int len = num.length;
int p = len - 2;
while (p >= 0 && num[p] >= num[p + 1]) {
p--;
}
if (p < 0) {
Arrays.sort(num);
} else {
int k = len - 1;
while (k >= 0 && num[k] <= num[p]) {
k--;
}
swap(num, p, k);
reverse(num, p + 1, len - 1);
}
}
private void swap(int[] num, int p, int k) {
num[p] = num[p] + num[k];
num[k] = num[p] - num[k];
num[p] = num[p] - num[k];
}
private void reverse(int[] num, int s, int d) {
while (s < d) {
swap(num, s++, d--);
}
}
Previous Permutation
Plz look at the new post.
Palindrome Partitioning
一次通关 again!very 高兴。
public ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> partition(String s) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> ans = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
boolean[][] map = palinMap(s);
helper(ans, new ArrayList<String>(), s, map, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> ans, ArrayList<String> path, String s, boolean[][] map, int pos) {
int len = s.length();
if (pos == len) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<String>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < len; i++) {
if (!map[pos][i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(s.substring(pos, i + 1));
helper(ans, path, s, map, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
private boolean[][] palinMap(String s) {
int len = s.length();
boolean[][] map = new boolean[len][len];
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
if (i > j) {
continue;
} else if (i == j) {
map[i][j] = true;
} else if (j - i == 1) {
map[i][j] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j);
} else {
map[i][j] = map[i + 1][j - 1] &
s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j);
}
}
}
return map;
}
Palindrome Partitioning II
This is DP, not Graph & Search.
Combination Sum
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (candidates == null || candidates.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
helper(ans, new ArrayList<Integer>(), candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ans, ArrayList<Integer> path,
int[] candidates, int target, int pos) {
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
} else if (target < 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target < candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
helper(ans, path, candidates, target - candidates[i], i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
Combination Sum II
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
if (candidates == null || candidates.length == 0) {
return ans;
}
Arrays.sort(candidates);
helper(ans, new ArrayList<Integer>(), candidates, target, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ans, ArrayList<Integer> path,
int[] candidates, int target, int pos) {
if (target == 0) {
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
} else if (target < 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = pos; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target < candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
if (i > pos && candidates[i - 1] == candidates[i]) {
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
helper(ans, path, candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
Word Ladder
Note that this is a BFS question, not DFS. I made it wrong and it took me a long time.
public int ladderLength(String start, String end, Set<String> dict) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
queue.add(start);
int length = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currentSize = queue.size();
for (int k = 0; k < currentSize; k++) {
String word = queue.remove();
// insert all adjacent strings of word
if (word.equals(end)) {
return length;
}
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char[] letters = word.toCharArray();
char originalLetter = letters[i];
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++) {
if (c == originalLetter) continue;
letters[i] = c;
String newLetters = String.valueOf(letters);
if (dict.contains(newLetters)) {
queue.add(newLetters);
dict.remove(newLetters);
}
}
letters[i] = originalLetter;
}
}
length++;
}
return 0;
}
Word Ladder II
unsolvable
Additional questions
Restore IP Addresses
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>();
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return ans;
}
helper(ans, new ArrayList<String>(), s, 0);
return ans;
}
private void helper(List<String> ans, List<String> path, String s, int pos) {
if (path.size() == 4) {
if (pos == s.length()) {
ans.add(convert(path));
}
return;
}
for (int i = pos + 1; i <= s.length() && i <= pos + 3; i++) {
String nextNum = s.substring(pos, i);
if (!isValid(nextNum)) {
continue;
}
path.add(nextNum);
helper(ans, path, s, i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
private boolean isValid(String str) {
if (str.length() == 1) {
return true;
} else if (str.charAt(0) == '0') {
return false;
} else {
int num = Integer.parseInt(str);
return 0 <= num && num <= 255;
}
}
private String convert(List<String> path) {
String str = "";
for (String s: path) {
str += "." + s;
}
return str.substring(1);
}
Combinations
skip
Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
skip
Permutation Sequence
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int fact = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
list.add(i);
fact *= i;
}
String ans = "";
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
fact = fact / i;
int rank = (k - 1) / fact;
k = (k - 1) % fact + 1;
int curNum = list.remove(rank);
ans += String.valueOf(curNum);
}
return ans;
}
Conclusion
DFS (O(2n), O(n!))
- Find all possible solutions
- Permutations / Subsets
BFS (O(m), O(n))
- Graph traversal
- Find shortest path in a simple graph
Two most canonical BFS questions:
- Graph traversal and toposort
- Word Ladder